Set up your patients for successful SCIG infusions


Educate patients and caregivers on how to perform SCIG infusions and answer any questions they may have

Teach self-infusion in a systematic, stepwise manner. Share the self-infusion video with your patients

Follow up with patients regarding any issues with self-infusions

Adjust the infusion process as necessary by changing:
- Needle gauge or length
- Location or number of infusion sites
- Infusion tubing
Oral hydration may decrease systemic adverse reactions.2 Unless otherwise instructed, encourage patients to drink water before their infusion.

Download Quick Reference Guide
Our SCIG quick reference guide can help get your patients started.

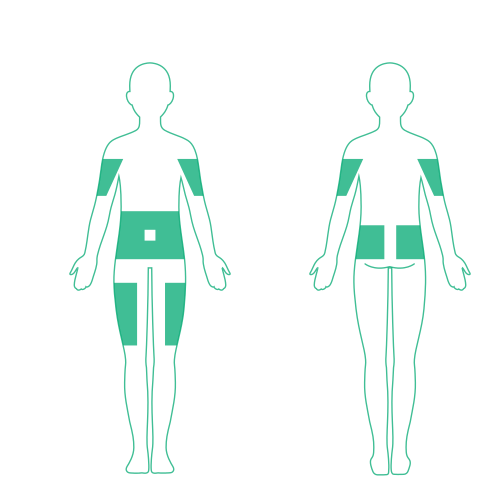
Consider a variety of factors when selecting infusion sites for XEMBIFY
- Select areas with adequate subcutaneous tissue3
- Ensure sites are at least 2 inches apart4
- Rotate the sites4
- Up to 6 sites can be used simultaneously4
NOTE: Infuse XEMBIFY in the abdomen, thigh, upper arm, sides, back, and/or lateral hip. Avoid bony areas, scars, areas of inflammation, superficial infection, or blood vessels.3,4
What to look for during and after SCIG administration
Check infusion sites for local adverse reactions such as erythema, discomfort, and swelling3
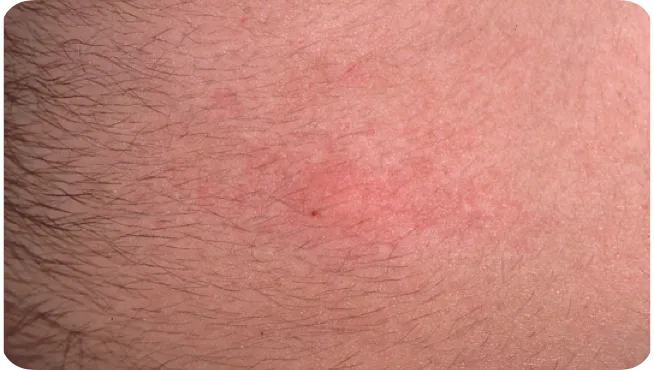
Mild infusion-site reaction
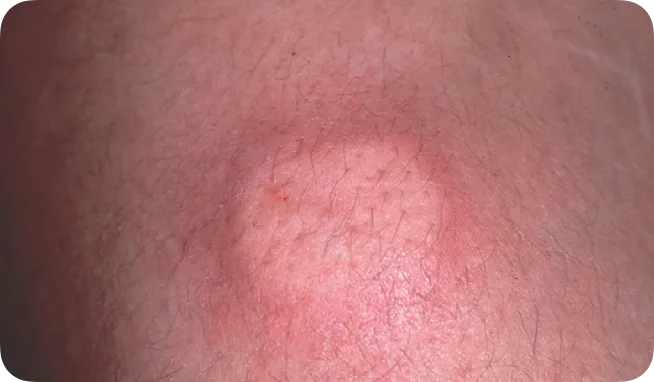
Moderate infusion-site reaction
Troubleshooting infusion-site reactions
- Make sure your patient is following appropriate dry needle insertion technique5
- Consider changing needle length if there is pain or leakage at the infusion site6
- Make sure infusion sites are 2 inches apart and 2 inches from navel3
- Make sure patient is rotating sites5
- Monitor the amount of fluid per site; maximum amount is 25 mL/site4
- Allow XEMBIFY to come to room temperature (68 to 77 ºF)4
Talking to your patients about starting XEMBIFY
- More than 90% of patients with commercial insurance have coverage for XEMBIFY7
- Patients who enroll in Xembify ConnexionsTM have access to a representative who can educate them about XEMBIFY and identify their coverage options
- Patients without insurance may be eligible to access XEMBIFY for free through the Patient Assistance Program
XEMBIFY Nurse Educators provide customized training and education
The Nurse Educator program is part of our commitment to empowering nurses and other clinicians by giving them the information and tools they need to successfully administer XEMBIFY.


Not actual size.
Ordering XEMBIFY
To order XEMBIFY 20% Injection Single-Use Vial

XEMBIFY partner distributors
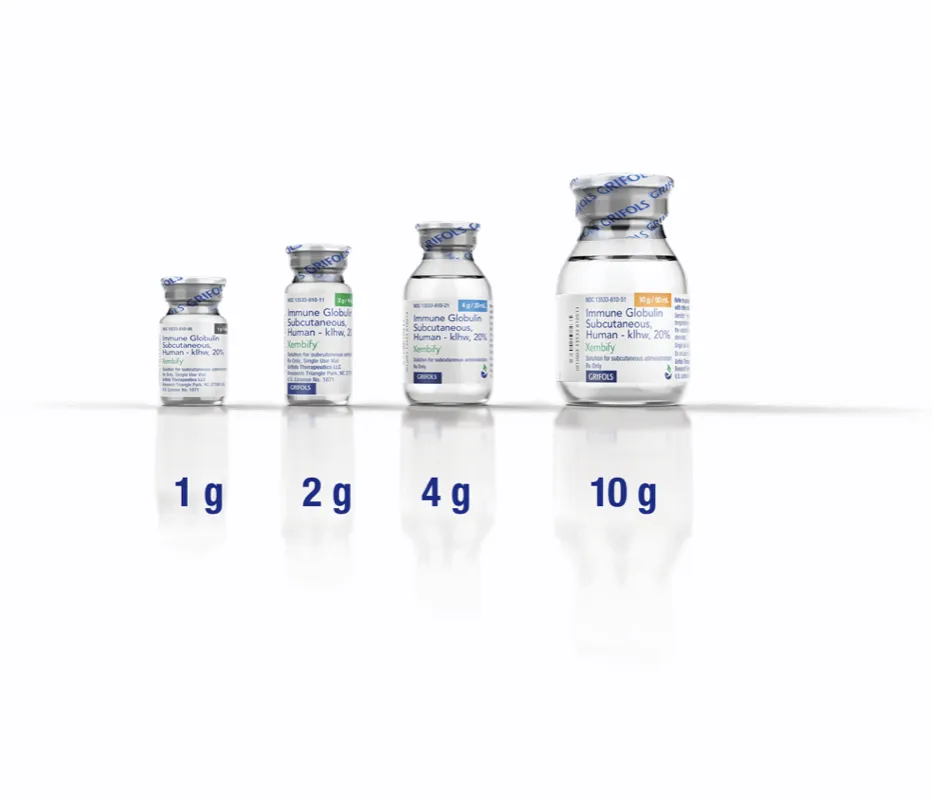
XEMBIFY vial sizes and corresponding NDCs4
13533-0810-05
- Size
-
5-mL vial
- Gram Protein
-
1 g
13533-0810-10
- Size
-
10-mL vial
- Gram Protein
-
2 g
13533-0810-20
- Size
-
20-mL vial
- Gram Protein
-
4 g
13533-0810-50
- Size
-
50-mL vial
- Gram Protein
-
10 g
| Package NDC | Size | Gram Protein |
|---|---|---|
|
13533-0810-05 |
5-mL vial |
1 g |
|
13533-0810-10 |
10-mL vial |
2 g |
|
13533-0810-20 |
20-mL vial |
4 g |
|
13533-0810-50 |
50-mL vial |
10 g |
Find out more about XEMBIFY—speak to a Sales Representative, Nurse Educator, or Medical Science Liaison.
Indication
XEMBIFY® (immune globulin subcutaneous human–klhw) is a 20% immune globulin indicated for treatment of primary humoral immunodeficiency disease (PIDD) in patients 2 years of age and older. XEMBIFY is for subcutaneous administration only.
Important Safety Information
WARNING: THROMBOSIS
- Thrombosis may occur with immune globulin products, including XEMBIFY. Risk factors may include: advanced age, prolonged immobilization, hypercoagulable conditions, history of venous or arterial thrombosis, use of estrogens, indwelling vascular catheters, hyperviscosity, and cardiovascular risk factors. Thrombosis may occur in the absence of known risk factors
- For patients at risk of thrombosis, administer XEMBIFY at the minimum dose and infusion rate practicable. Ensure adequate hydration in patients before administration. Monitor for signs and symptoms of thrombosis and assess blood viscosity in patients at risk of hyperviscosity
Contraindications
XEMBIFY is contraindicated in patients who have had an anaphylactic or severe systemic reaction to the administration of human immune globulin. It is contraindicated in IgA-deficient patients with antibodies against IgA and a history of hypersensitivity.
Warnings and Precautions
Aseptic meningitis syndrome (AMS). AMS may occur with human immune globulin treatment, including XEMBIFY. Conduct a thorough neurological exam on patients exhibiting signs and symptoms to rule out other causes of meningitis. Discontinuation of treatment has resulted in remission within several days without sequelae.
Thrombosis. Thrombosis may occur following treatment with immune globulin products, including XEMBIFY. Thrombosis may occur in the absence of known risk factors. In patients at risk, administer at the minimum dose and infusion rate practicable. Ensure adequate hydration before administration. Monitor for signs and symptoms of thrombosis and assess blood viscosity in patients at risk of hyperviscosity.
Hypersensitivity. Severe hypersensitivity reactions may occur with immune globulin products, including XEMBIFY. In case of hypersensitivity, discontinue infusion immediately and institute appropriate treatment. XEMBIFY contains IgA. Patients with known antibodies to IgA may have a greater risk of developing potentially severe hypersensitivity and anaphylactic reactions.
Renal dysfunction/failure. Acute renal dysfunction/failure, acute tubular necrosis, proximal tubular nephropathy, osmotic nephrosis, and death may occur with use of human immune globulin products, especially those containing sucrose. XEMBIFY does not contain sucrose. Ensure patients are not volume-depleted prior to starting infusion. In patients at risk due to preexisting renal insufficiency or predisposition to acute renal failure, assess renal function prior to the initial infusion of XEMBIFY and again at appropriate intervals thereafter. If renal function deteriorates, consider discontinuation.
Hemolysis. XEMBIFY may contain blood group antibodies that may cause a positive direct antiglobulin reaction and hemolysis. Monitor patients for clinical signs and symptoms of hemolysis. If signs and symptoms are present after infusion, perform confirmatory lab testing.
Transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI). Noncardiogenic pulmonary edema may occur in patients following treatment with immune globulin products, including XEMBIFY. Monitor patients for pulmonary adverse reactions. If TRALI is suspected, perform appropriate tests for the presence of antineutrophil and anti-HLA antibodies in both the product and patient serum. TRALI may be managed using oxygen therapy with adequate ventilatory support.
Transmissible infectious agents. Because XEMBIFY is made from human blood, it may carry a risk of transmitting infectious agents, eg, viruses, the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) agent, and, theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) agent. No cases of transmission of viral diseases, vCJD, or CJD have ever been associated with the use of XEMBIFY.
Interference with lab tests. After infusion of XEMBIFY, passively transferred antibodies in the patient’s blood may yield positive serological testing results, with the potential for misleading interpretation.
Adverse Reactions
The most common adverse reactions in ≥ 5% of subjects in the clinical trial were local adverse reactions, including infusion-site erythema (redness), infusion-site pain, infusion-site swelling (puffiness), infusion-site bruising, infusion-site nodule, infusion-site pruritus (itching), infusion-site induration (firmness), infusion-site scab, infusion-site edema, and systemic reactions including cough and diarrhea.
Drug Interactions
Passive transfer of antibodies may transiently interfere with the immune responses to live attenuated virus vaccines (eg, measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella).
Please see full Prescribing Information for XEMBIFY.
Terms to know
IG, immune globulin; NDC, National Drug Code; PIDD, primary humoral immunodeficiency disease; SCIG, subcutaneous immunoglobulin.
References
- Jolles S, Orange J, Gardulf A, et al. Current treatment options with immunoglobulin G for the individualization of care in patients with primary immunodeficiency disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 2015;179(2):146-160.
-
Ballow M, Epland K, Heimall J, et al. Immune Deficiency Foundation Patient & Family Handbook for Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases. 6th ed. Immune Deficiency Foundation; 2019.
-
Immunoglobulin National Society. Immunoglobulin Therapy: Standards of Practice. 3.2 ed. Ig Society, Inc.; 2024.
-
XEMBIFY Prescribing Information, Grifols. July 2024.
-
Immune Deficiency Foundation. IDF Guide for Nurses: Immunoglobulin Therapy for Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases. 4th ed. Immune Deficiency Foundation; 2016.
-
Alberta Health Services. Home Infusion of Subcutaneous Immune Globulin (SCIG).
-
Data on file, Grifols.