Customizable and consistent dosing for your patients with no titration required1


Consistency
Steady infusion rate up to 35 mL/hr/site,* customizable from the start1

Confidence
Favorable tolerability and safety profile for treatment-naive or treatment-experienced patients1,2

Reassurance
Tailored dosing schedule, up to every 2 weeks1
XEMBIFY delivers proven tolerability with dosing flexibility that meets your patients’ needs1
SCIG therapy with customizable dosing up to 35 mL/hr/site* from the start1
- SCIG from the start for treatment-naive patients
- Seamless switch from IVIG or another SCIG
- Infusion rates up to 35 mL/hr/site*
- No titration required
- Up to 6 infusion sites with maximum volume 25 mL/site
XEMBIFY offers patients with PIDD flexibility and options1
Convenient handling and storage1
- No refrigeration needed for up to 6 months1‡
- Check the lot number, expiration date, tamper-evident seal, color and clarity, and storage temperature before infusion of XEMBIFY1,3
- Never shake XEMBIFY1
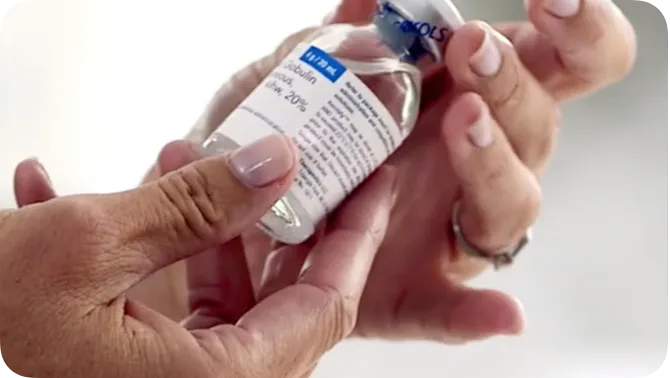
- Available in 1-g, 2-g, 4-g, and 10-g single-use vials1‡

Patients receiving XEMBIFY can start and stay at the same infusion rate1
Infusion rate: up to 35 mL/hr/site*
Number of sites: up to 6 infusion sites with maximum volume of 25 mL/site
Site distance: at least 2 inches apart
No titration required
- Children may require less total volume for a specific XEMBIFY dose (mg/kg body weight) than adults
- You may choose a smaller volume/site for children and/or fewer infusion sites to achieve the target total dose, depending on the needs of the child
- Children 2 to < 10 years of age have a maximum infusion rate of 25/mL/hr/site

XEMBIFY self-infusion instructional video
This video demonstrates step-by-step instructions for self-infusing XEMBIFY for patients with PIDD.

Treatment with XEMBIFY can benefit a range of patients
Examples of patients starting treatment with XEMBIFY
Tessa
Tessa is a sixth-grade schoolteacher who is married with 2 children and has been diagnosed with CVID. She has poorly controlled asthma and a history of migraine. Tessa recently started antibiotic therapy due to chronic sinusitis and multiple episodes of bacterial pneumonia. She needs an IG treatment like XEMBIFY that has a low incidence of headaches.
Tessa’s customized dosing schedule with XEMBIFY§:
Dosing frequency and interval: every 2 weeks
Every-2-weeks dose║: 20 g (100 mL)
Number of infusion sites: 4
Infusion rate: 35 mL/hr/site
Infusion time: ~50 minutes, depending on regulator used

Not an actual patient.
Jenna
Jenna is a 14-year-old freshman in high school with CVID. She loves sports and hanging out with her friends. She experiences lethargy and malaise before her next dose of IVIG, consistent with “wear-off” effect.
Jenna's customized dosing schedule with XEMBIFY§:
Dosing frequency and interval: once weekly
Weekly dose║: 10 g (50 mL)
Number of infusion sites: 2
Infusion rate: 25 mL/hr/site
Infusion time: ~1 hour, depending on regulator used

Not an actual patient.
Hayden
Hayden is a happy and active 6-year-old boy. He attends school 5 days a week and enjoys sharing toys and playing with his friends. Since he was 6 months old, Hayden has suffered from recurrent otitis and chronic cough. Hayden’s physician has confirmed a diagnosis of PIDD.
Hayden’s customized dosing schedule with XEMBIFY§:
Dosing frequency and interval: once weekly
Weekly dose║: 3 g (15 mL)
Number of infusion sites: 1
Infusion rate: 10 mL/hr/site
Infusion time: ~1-2 hours, depending on regulator used

Not an actual patient.
*Children 2 to <10 years of age have a maximum infusion rate of 25 mL/hr/site.1
†XEMBIFY can be administered at regular intervals from daily up to every 2 weeks.1
‡XEMBIFY may be stored for 36 months at 2 to 8 °C (36 to 46 °F) from the date of manufacture and the product may be stored at temperatures not to exceed 25 °C (77 °F) for up to 6 months any time prior to the expiration date. Following 25 °C (77 °F) storage, use the product immediately or discard. Do not freeze.1,4
§To convert the XEMBIFY dose in grams to milliliters (mL), multiply the calculated initial SCIG dose in grams by 5.1
║Initial weekly dose of SCIG in grams = prior IVIG in grams/number of weeks between IVIG doses x 1.37.1
Find out more about XEMBIFY—speak to a Sales Representative, Nurse Educator, or Medical Science Liaison.
Indication
XEMBIFY® (immune globulin subcutaneous human–klhw) is a 20% immune globulin indicated for treatment of primary humoral immunodeficiency disease (PIDD) in patients 2 years of age and older. XEMBIFY is for subcutaneous administration only.
Important Safety Information
WARNING: THROMBOSIS
- Thrombosis may occur with immune globulin products, including XEMBIFY. Risk factors may include: advanced age, prolonged immobilization, hypercoagulable conditions, history of venous or arterial thrombosis, use of estrogens, indwelling vascular catheters, hyperviscosity, and cardiovascular risk factors. Thrombosis may occur in the absence of known risk factors
- For patients at risk of thrombosis, administer XEMBIFY at the minimum dose and infusion rate practicable. Ensure adequate hydration in patients before administration. Monitor for signs and symptoms of thrombosis and assess blood viscosity in patients at risk of hyperviscosity
Contraindications
XEMBIFY is contraindicated in patients who have had an anaphylactic or severe systemic reaction to the administration of human immune globulin. It is contraindicated in IgA-deficient patients with antibodies against IgA and a history of hypersensitivity.
Warnings and Precautions
Aseptic meningitis syndrome (AMS). AMS may occur with human immune globulin treatment, including XEMBIFY. Conduct a thorough neurological exam on patients exhibiting signs and symptoms to rule out other causes of meningitis. Discontinuation of treatment has resulted in remission within several days without sequelae.
Thrombosis. Thrombosis may occur following treatment with immune globulin products, including XEMBIFY. Thrombosis may occur in the absence of known risk factors. In patients at risk, administer at the minimum dose and infusion rate practicable. Ensure adequate hydration before administration. Monitor for signs and symptoms of thrombosis and assess blood viscosity in patients at risk of hyperviscosity.
Hypersensitivity. Severe hypersensitivity reactions may occur with immune globulin products, including XEMBIFY. In case of hypersensitivity, discontinue infusion immediately and institute appropriate treatment. XEMBIFY contains IgA. Patients with known antibodies to IgA may have a greater risk of developing potentially severe hypersensitivity and anaphylactic reactions.
Renal dysfunction/failure. Acute renal dysfunction/failure, acute tubular necrosis, proximal tubular nephropathy, osmotic nephrosis, and death may occur with use of human immune globulin products, especially those containing sucrose. XEMBIFY does not contain sucrose. Ensure patients are not volume-depleted prior to starting infusion. In patients at risk due to preexisting renal insufficiency or predisposition to acute renal failure, assess renal function prior to the initial infusion of XEMBIFY and again at appropriate intervals thereafter. If renal function deteriorates, consider discontinuation.
Hemolysis. XEMBIFY may contain blood group antibodies that may cause a positive direct antiglobulin reaction and hemolysis. Monitor patients for clinical signs and symptoms of hemolysis. If signs and symptoms are present after infusion, perform confirmatory lab testing.
Transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI). Noncardiogenic pulmonary edema may occur in patients following treatment with immune globulin products, including XEMBIFY. Monitor patients for pulmonary adverse reactions. If TRALI is suspected, perform appropriate tests for the presence of antineutrophil and anti-HLA antibodies in both the product and patient serum. TRALI may be managed using oxygen therapy with adequate ventilatory support.
Transmissible infectious agents. Because XEMBIFY is made from human blood, it may carry a risk of transmitting infectious agents, eg, viruses, the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) agent, and, theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) agent. No cases of transmission of viral diseases, vCJD, or CJD have ever been associated with the use of XEMBIFY.
Interference with lab tests. After infusion of XEMBIFY, passively transferred antibodies in the patient’s blood may yield positive serological testing results, with the potential for misleading interpretation.
Adverse Reactions
The most common adverse reactions in ≥ 5% of subjects in the clinical trial were local adverse reactions, including infusion-site erythema (redness), infusion-site pain, infusion-site swelling (puffiness), infusion-site bruising, infusion-site nodule, infusion-site pruritus (itching), infusion-site induration (firmness), infusion-site scab, infusion-site edema, and systemic reactions including cough and diarrhea.
Drug Interactions
Passive transfer of antibodies may transiently interfere with the immune responses to live attenuated virus vaccines (eg, measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella).
Please see full Prescribing Information for XEMBIFY.
Terms to know
CVID, common variable immunodeficiency; hr, hour; IG, immune globulin; IgG, immunoglobulin G; IVIG, intravenous immunoglobulin; PIDD, primary humoral immunodeficiency disease; SCIG, subcutaneous immunoglobulin.
References
- XEMBIFY Prescribing Information, Grifols. July 2024.
- Sleasman JW, Lumry WR, Hussain I, et al. Immune globulin subcutaneous, human - klhw 20% for primary humoral immunodeficiency: an open-label, phase III study. Immunotherapy. 2019;11(16):1371-1386.
- Immunoglobulin National Society. Immunoglobulin Therapy: Standards of Practice. 3.2 ed. Ig Society, Inc.; 2024.
- Data on file, Grifols.